A Microscopic View on Quantum Fluctuations
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics achieve direct imaging of quantum fluctuations at absolute zero temperature
The scientists start by cooling a small cloud of rubidium atoms down to a temperature near absolute zero, about minus 273 degree Celsius. The ensemble is then subjected to a light field that severely restricts the motion of the particles along one-dimensional tubes of light aligned in parallel. An additional standing laser wave along the tubes creates a one-dimensional optical lattice that holds the atoms in a periodic array of bright and dark regions of light.
The atoms move in the periodic light field like electrons in solids. As these can be electric conductors or insulators, also the one-dimensional quantum gases can behave like a superfluid or like an insulator at low temperatures. In particular, the height of the optical lattice potential plays an important role: it determines whether the atom is fixed on a particular lattice site or whether it is able to move to a neighbouring site. At very large lattice depths, each lattice site is occupied by exactly one atom. This highly ordered state is called a “Mott insulator”, after the British physicist and Nobel laureate Sir Neville Mott. When the lattice depth is decreased slightly, the atoms have enough energy to reach a neighbouring site by quantum mechanical tunneling. In this way, pairs of empty and doubly occupied sites emerge, so-called particle-hole pairs. Intriguingly, these quantum fluctuations also occur at absolute zero temperature, when all movement in the classical world is frozen out. The position of the quantum-correlated particle-hole pairs in the crystal is completely undetermined and is fixed only by the measurement process.
In recent experiments, the physicists around Stefan Kuhr and Immanuel Bloch had already developed a method, which allowed to image single atoms lattice site by lattice site. The atoms are cooled using laser beams, and the fluorescence photons emitted in this process are used to observe the atoms with a high resolution microscope. Holes naturally show up as dark spots, but so do doubly occupied sites as the two particles kick each other out of the lattice in the experiment. Therefore particle-hole pairs appear as two neighbouring dark lattice sites (see figure below). “With our technique, we can directly observe this fundamental quantum phenomenon for the first time”, describes doctoral student Manuel Endres enthusiastically.
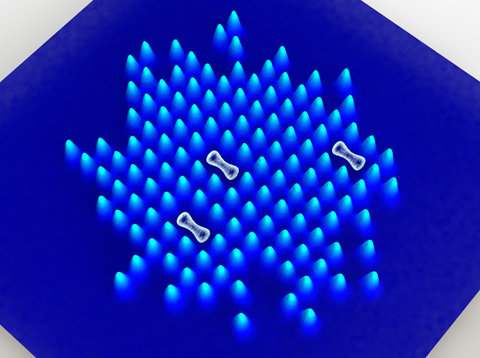
Figure: Schematic view of the atom distribution in the optical lattice. Quantum fluctuations (white) are directly visible as neighbouring dark spots. (High resolution images available at: www.quantum-munich.de/media/.)
The physicists measure the number of neighbouring particle-hole pairs through a correlation function. With increasing kinetic energy, more and more particles tunnel to neighbouring sites and the pair correlations increase. However, when the number of particle-hole pairs is very large, it becomes difficult to unambiguously identify them. Hence the correlation function takes on smaller values. Finally, the ordered state of a Mott insulator vanishes completely und the quantum gas becomes a superfluid. Here fluctuations of holes and particles occur independently. The correlation function measured in the experiment is very well reproduced by model calculations, which were performed by scientists from the Theory Division at the MPQ and the ETH Zurich. Interestingly, the same investigations on two-dimensional quantum-gases clearly showed that quantum fluctuations are not as prominent as in one-dimensional systems.
The scientists extended their analysis to correlations between several lattice sites along a string. Such non-local correlation functions contain important information about the underlying many-body system and can be used as an order parameter to characterize different quantum phases. In the experiment described here, such non-local order parameters have been measured for the first time. In the future, the scientists plan to use these measurements for the detection of topological quantum phases. These can be useful for robust quantum computers and could help to understand superconductivity at high temperatures. Olivia Meyer-Streng
Contact:Prof. Dr. Immanuel Bloch
Chair of Quantum Optics, LMU Munich
Schellingstr. 4, 80799 Munich, Germany
Director at Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics
Hans-Kopfermann-Straße 1, 85748 Garching
Phone: +49 (0)89 / 32 905 -138
E-mail: immanuel.bloch@mpq.mpg.de
Prof. Dr. Stefan Kuhr
University of Strathclyde, Department of Physics
107 Rottenrow East, Glasgow G4 0NG, U.K.
Phone: +44 141-548-3364
E-mail: stefan.kuhr@strath.ac.uk
Manuel Endres
Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics
Hans-Kopfermann-Straße 1, 85748 Garching
Phone: +49 (0)89 / 32 905 -214
E-mail: manuel.endres@mpq.mpg.de
Dr. Olivia Meyer-Streng
Press & Public Relations
Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics
Phone: +49 (0)89 / 32 905 -213
E-mail: olivia.meyer-streng@mpq.mpg.de